
The role of innovation across the NDA group
A vital part of the NDA’s mission is driving innovation in nuclear decommissioning to help address the wide-ranging, complex challenges across all our sites and businesses.
We already do a lot of valuable work to develop technology which will support our mission, but are committed to taking more of a visible leadership role. Sharing our grand challenges for technical innovation is an important step on that journey.
Our current approach to Research and Development (R&D)
The majority of R&D and innovation is carried out by our Site Licence Companies (SLCs), subsidiaries and their suppliers - to address specific challenges.
At the NDA Corporate Centre, we also commission a portfolio of development work directly from the supply chain. This ‘strategic portfolio’, currently totalling approximately £8 million, addresses common needs or opportunities across multiple sites and forms an important part of the overall R&D budget which, in financial year 2018 to 2019, totalled £90 million.
The focus of the NDA’s strategic R&D and innovation portfolio is:
- helping to shape and underpin NDA group strategies
- delivering R&D and early innovation across multiple sites
- developing vital technical expertise for the future
As a key customer for innovative solutions, a significant funder of R&D and, as a body with strategic oversight of the UK’s civil nuclear sites, the NDA is in a unique position.
We understand the common barriers we face across the group and help to identify the areas where innovative approaches, and the adoption of new technologies, can bring value. As well as continuing to work in close collaboration with the site licensees and subsidiaries, we also work with a number of other government departments on a range of specific projects. More recently, we have started to actively reach out to other industrial sectors and their supply chains – an area we want to develop further.
In the spirit of a ‘Grand Challenge’...
Grand Challenges, by their nature, should be bold, cross-cutting, disruptive and set a direction of travel - while not being unrealistic. They are not about implementing continuous improvement or incremental efficiencies as part of business-as-usual activities. They should involve missions, be ambitious and time-bound, thereby producing multiple solutions which drive innovation and change.

As part of our desire to drive innovation, and support the work already underway within the supply chain to implement the Nuclear Sector Deal, we are pleased to publish our very own Grand Challenges for Technical Innovation. These are intended to alter the status quo, have a broad appeal and provide an opportunity to collaborate and engage across sites and with other industries, government departments and with overseas partners.
They set out a broad vision of the future, set our aspirations and aims and also include a challenging deadline - to inject a sense of pace.
Engaging our people
We launched an internal consultation across the NDA group in August 2019, engaging technical experts as well as inviting participation from anyone in the group who had a good idea.
Good ideas can come from anywhere and we can do much more to stimulate discussion, encourage creativity and engage more widely. We need to learn from our past but also actively encourage diversity of thought, if we wish to take a leading role and be part of a sector where innovation can truly thrive.
The technical challenge themes
Over 100 ideas and responses were received from across the NDA group and beyond. Four overarching themes emerged where technical innovation could deliver significant benefits:
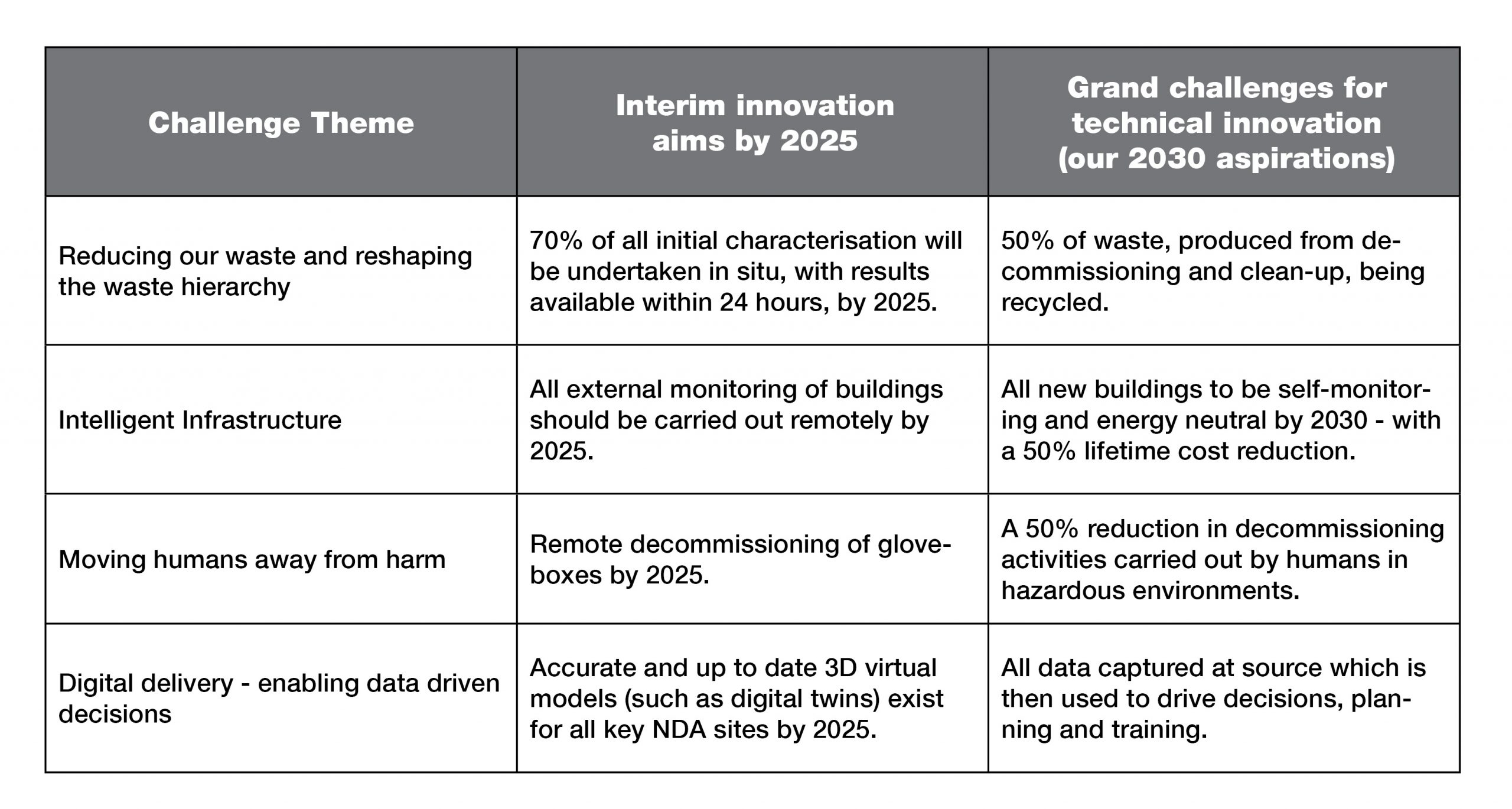
- reducing our waste and reshaping the waste hierarchy - finding new ways to drive value by proactively applying the waste hierarchy to the entirety of the NDA group inventory (active and non-active wastes), reducing consumption of resources, increasing recycling and re-use in order to reduce volumes sent for disposal. This could include new sensing techniques, multi-mode logistics, different treatment methods and optimising sorting and packaging approaches (remote sorting and smart packaging).
- intelligent infrastructure – using autonomous technology to monitor and manage assets and buildings efficiently. This could include new construction approaches (materials, modularisation, off-site build), smart stores and packages, and improving reliability and availability through the adoption of enhanced technologies which enable more proactive management practices and predictive, improved performance.
- moving humans away from harm – reducing the need for people to enter hazardous environments (including radioactive, working at height, asbestos) by making more use of autonomous systems, sensors and robotics. Where entry is required, making better use of enhanced training environments, wearable technologies and augmented reality.
- digital delivery - adopting modern technology for capturing, assuring and using data efficiently, to improve planning, immersive training and to aid decision-making, making more use of machine learning and artificial intelligence to enhance assurance or to help simplify data intensive processes.
These technical challenge themes are intentionally broad in nature and are applicable across the NDA group, across different market sectors and also have wider societal benefit. There will be areas where the nuclear sector excels and would naturally want to take a lead in driving innovation (such as radioactive waste and radiation-related safety). For other topics, such as infrastructure management, construction and digital, as well as engaging with the nuclear sector, we will be actively seeking to collaborate and partner, leveraging investment and developments by working alongside other sectors.
We want to encourage and use a ‘best athlete’ approach to innovation - ensuring we adopt with pride the good ideas and practices, irrespective of their origin.
Our aspirations for technical innovation
Our 2030 aspirations will inform our NDA group-wide innovation programmes, but we have also set some interim aims for implementation by 2025. These build on existing R&D work, where component solutions are known to exist. We hope this will provide the catalyst to develop more integrated systems and services, which will enable faster adoption into business-as-usual operations.
Although the challenges are intended to be ‘solution agnostic’, we expect a number of key emerging technologies will play a significant role including: advanced robotics, artificial intelligence, autonomous systems, adaptive wearables, smart sensors, advanced photonics, new materials, treatment processes, digital and next generation connectivity solutions.
 Next steps
Next steps
In publishing our challenges and setting out our current aspirations, we are presenting our intended direction of travel and the timeframes over which the NDA group wants to see innovation delivering change and benefit. These are challenging timescales and we expect, as we engage and make progress, that our plans will naturally evolve and improve.
We welcome feedback on these challenges and will be discussing them in more detail with key stakeholders, including the industry led Nuclear Sector Deal Working Groups, over the coming weeks. The NDA is currently defining its future innovation programmes in line with these grand challenges.
If you’d like to know more, please leave a comment for me below.
2 comments
Comment by Hoke Shuler posted on
I would like to run a few test to see if we can reduce you nuclear waste. Would you send me the exact nuclear waste you are storing. Once I have the particular type of nuclear waste and isotope, we will use our test facilities here, in the US, to test an identical waste and isotope to see if we can help.
Thank you,
HokeShuler@gmail.com
Comment by deborahward posted on
The most comprehensive information available about radioactive waste in the UK can be found at: https://ukinventory.nda.gov.uk/
Updated every three years, this inventory covers radioactive waste from all across the UK. The reports contain information on quantities that exist now and are forecast to arise in the future, as well as details of specific waste types.